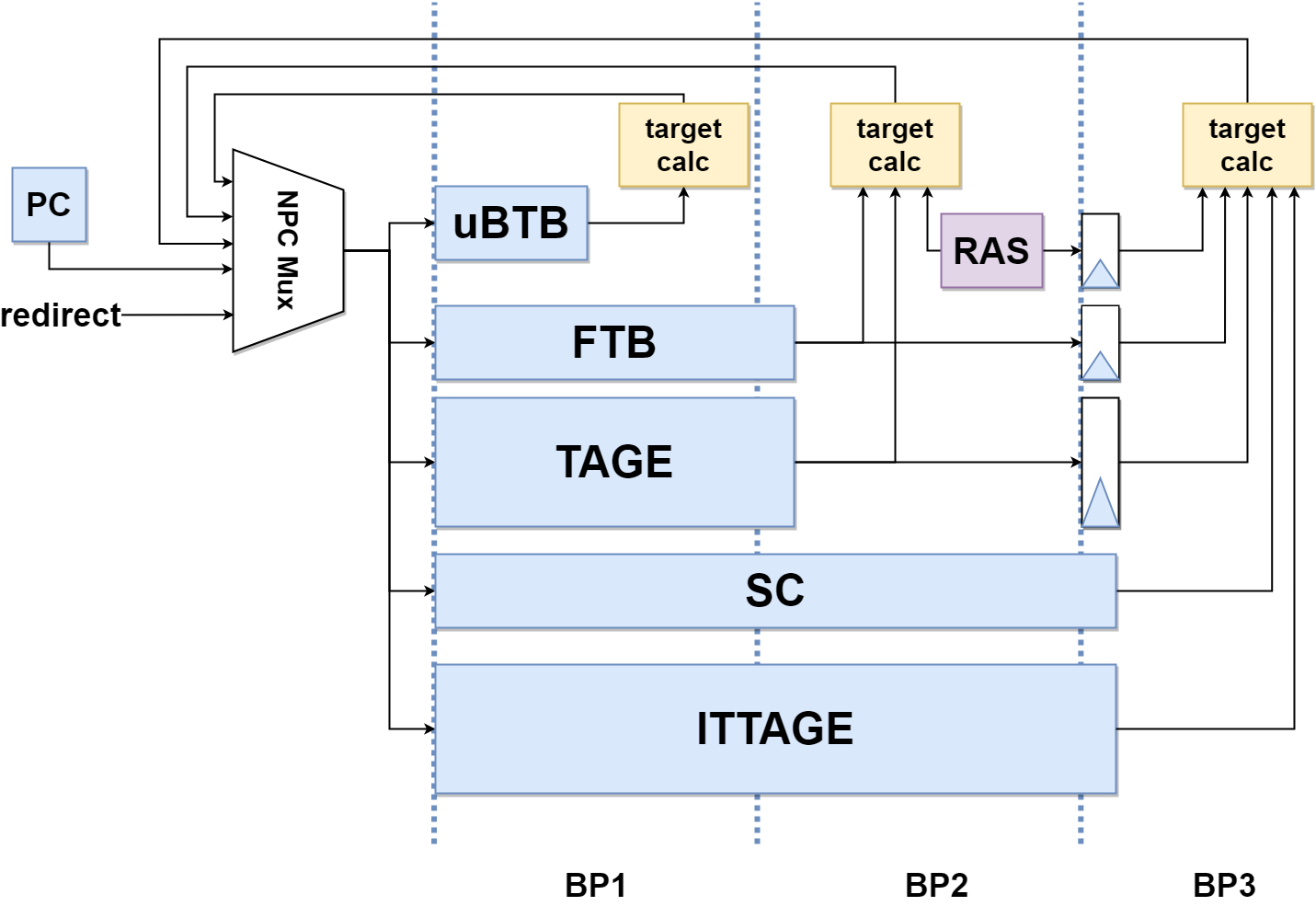
ITTAGE
概述
源代码:/xiangshan/frontend/ITTAGE.scala
ITTAGE是xiangshan中用于预测间接跳转(jalr)跳转目标地址的预测器。如果是基于函数返回的jalr,xiangshan规定由RAS来进行预测,其他的间接跳转则交由ITTAGE来进行预测。
ITTAGE Table
参数
ITTageTableInfos: Seq[Tuple3[Int,Int,Int]] =
// Sets Hist Tag
Seq(( 256, 4, 9),
( 256, 8, 9),
( 512, 13, 9),
( 512, 16, 9),
( 512, 32, 9)),
IO
ITTageReq是ITTAGE的输入请求,比较简单,其定义如下所示:
class ITTageReq(implicit p: Parameters) extends ITTageBundle {
val pc = UInt(VAddrBits.W)
val folded_hist = new AllFoldedHistories(foldedGHistInfos)
}
pc: 当前预测块的pc地址folded_hist: 折叠的全局分支历史
ITTageResp是ITTAGE的输出结果,其定义如下所示:
class ITTageResp(implicit p: Parameters) extends ITTageBundle {
val ctr = UInt(ITTageCtrBits.W) // ITTageCtrBits = 2
val u = UInt(2.W)
val target = UInt(VAddrBits.W)
}
ctr: ITTage计数器值,2位u: useful域值,2位target: 跳转目标地址
ITTageUpdate是ITTAGE的更新输入,其定义如下所示:
class ITTageUpdate(implicit p: Parameters) extends ITTageBundle {
val pc = UInt(VAddrBits.W)
val folded_hist = new AllFoldedHistories(foldedGHistInfos)
// update tag and ctr
val valid = Bool()
val correct = Bool()
val alloc = Bool()
val oldCtr = UInt(ITTageCtrBits.W)
// update u
val uValid = Bool()
val u = Bool()
val reset_u = Bool()
// target
val target = UInt(VAddrBits.W)
val old_target = UInt(VAddrBits.W)
}
xiangshan的ITTAGE中包含有ctr值以及useful域,因此更新的信息中还包含对ctr以及u的更新信息。
ITTageEntry
ITTageEntry定义ITTAGE每个表项的信息,其定义如下:
class ITTageEntry() extends ITTageBundle {
// val valid = Bool()
val tag = UInt(tagLen.W)
val ctr = UInt(ITTageCtrBits.W)
val target = UInt(VAddrBits.W)
}
tag: pc与折叠全局历史哈希后的tagctr: ITTAGE计数器值,2位target: 间接跳转目标地址
ITTAGE的idx以及tag的计算与TAGE类似,idx等于pc与折叠分支历史的哈希,而tag则为:
val tag = ((unhashed_idx >> log2Ceil(nRows)) ^ tag_fh ^ (alt_tag_fh << 1)) (tagLen - 1, 0)
alt_tag_fh实际上就是全局分支历史取hist length-1长左移1位后的折叠分支历史。(用于去除一些常见的全局分支历史pattern带来的影响)
SRAM
val SRAM_SIZE=128
val nBanks = 2
val bankSize = nRows / nBanks
val bankFoldWidth = if (bankSize >= SRAM_SIZE) bankSize / SRAM_SIZE else 1
val us = Module(new Folded1WDataModuleTemplate(Bool(), nRows, 1, isSync=true, width=uFoldedWidth))
val table_banks = Seq.fill(nBanks)(
Module(new FoldedSRAMTemplate(new ITTageEntry, set=nRows/nBanks, width=bankFoldWidth, shouldReset=false, holdRead=true, singlePort=true)))
对于useful域来说,实际上就是一个是否有效的比特位,在其对应存储的SRAM us中,每行存储16位,SRAM一共有nRows/16行。
对于ITTAGE entry表来说,其SRAM一共有2个bank,每个bank有nRows/nBanks行,每行有2(nRows=512)或1(nRows=256)路。
Resp
ITTAGE Table的resp比较直白,直接将从表中读取到的ctr、u以及target信息送到输出的ITTageResp接口中即可1。需要注意的是,在ITTAGE当中,即使出现读写冲突,也不会造成resp的无效化。
[1] 后面3张表,nRows=512,每个bank有2路,为什么会只选择data(0)?
val table_banks_r = table_banks.map(_.io.r.resp.data(0))
val resp_selected = Mux1H(s1_bank_req_1h, table_banks_r)
val s1_req_rhit = validArray(s1_idx) && resp_selected.tag === s1_tag
io.resp.valid := (if (tagLen != 0) s1_req_rhit else true.B) // && s1_mask(b)
io.resp.bits.ctr := resp_selected.ctr
io.resp.bits.u := us.io.rdata(0)
io.resp.bits.target := resp_selected.target
Update
与TAGE类似,ITTAGE的update同样存在bypass机制,在这里不再进行赘述。
ITTAGE的ctr值在allocate的时候,会赋予初值2。根据间接目标地址预测是否正确来调整ctr的值,正确+1,错误-1。
需要注意的是,当allocate或者ctr值为0时,会将后端给到的update target更新到间接跳转目标地址中,否则会保持旧值不变:
update_wdata.target := Mux(io.update.alloc || ctr_null(old_ctr), update_target, io.update.old_target)
ITTAGE top
Resp
ITTAGE信息反馈通过ITTageMeta类的实例来实现:
class ITTageMeta(implicit p: Parameters) extends XSBundle with ITTageParams{
val provider = ValidUndirectioned(UInt(log2Ceil(ITTageNTables).W))
val altProvider = ValidUndirectioned(UInt(log2Ceil(ITTageNTables).W))
val altDiffers = Bool()
val providerU = Bool()
val providerCtr = UInt(ITTageCtrBits.W)
val altProviderCtr = UInt(ITTageCtrBits.W)
val allocate = ValidUndirectioned(UInt(log2Ceil(ITTageNTables).W))
val taken = Bool()
val providerTarget = UInt(VAddrBits.W)
val altProviderTarget = UInt(VAddrBits.W)
// val scMeta = new SCMeta(EnableSC)
// TODO: check if we need target info here
val pred_cycle = if (!env.FPGAPlatform) Some(UInt(64.W)) else None
}
从5张ITTAGE表中选择最长命中的预测结果以及第二长的备选预测结果。base的预测则使用FTB中的预测:
val inputRes = VecInit(s2_resps.zipWithIndex.map{case (r, i) => {
val tableInfo = Wire(new ITTageTableInfo)
tableInfo.u := r.bits.u
tableInfo.ctr := r.bits.ctr
tableInfo.target := r.bits.target
tableInfo.tableIdx := i.U(log2Ceil(ITTageNTables).W)
SelectTwoInterRes(r.valid, tableInfo)
}})
val selectedInfo = ParallelSelectTwo(inputRes.reverse)
val provided = selectedInfo.hasOne
val altProvided = selectedInfo.hasTwo
val providerInfo = selectedInfo.first
val altProviderInfo = selectedInfo.second
val providerNull = providerInfo.ctr === 0.U
val basePred = true.B
val baseTarget = io.in.bits.resp_in(0).s2.full_pred.jalr_target // use ftb pred as base target
如果最长预测的ctr值非零,则使用最长预测命中的目标地址,若最长预测的ctr为0,则使用备选预测的目标地址,若都没有命中,则使用base的预测:
s2_tageTaken := Mux1H(Seq(
(provided && !providerNull, providerInfo.ctr(ITTageCtrBits-1)),
(altProvided && providerNull, altProviderInfo.ctr(ITTageCtrBits-1)),
(!provided, basePred)
)) // TODO: reintroduce BIM
s2_tageTarget := Mux1H(Seq(
(provided && !providerNull, providerInfo.target),
(altProvided && providerNull, altProviderInfo.target),
(!provided, baseTarget)
))
Update
Update ITTAGE的前提是,需要update的jalr指令不是ret指令(ret由RAS来预测):
val updateValid =
update.full_pred.is_jalr && !update.full_pred.is_ret && u_valid && update.ftb_entry.jmpValid &&
!(update.full_pred.real_br_taken_mask().reduce(_||_))
allocate与TAGE一致,找比最长预测还长的表中是否还有空位可以allocate。allocate的位置如果随机数结果包含在里面则使用随机的位置,否则使用第一个可用的位置(可以allocate里面长度最小的):
// Create a mask fo tables which did not hit our query, and also contain useless entries
// and also uses a longer history than the provider
val s2_allocatableSlots = VecInit(s2_resps.map(r => !r.valid && !r.bits.u)).asUInt &
~(LowerMask(UIntToOH(s2_provider), ITTageNTables) & Fill(ITTageNTables, s2_provided.asUInt))
val s2_allocLFSR = LFSR64()(ITTageNTables - 1, 0)
val s2_firstEntry = PriorityEncoder(s2_allocatableSlots)
val s2_maskedEntry = PriorityEncoder(s2_allocatableSlots & s2_allocLFSR)
val s2_allocEntry = Mux(s2_allocatableSlots(s2_maskedEntry), s2_maskedEntry, s2_firstEntry)
resp_meta.allocate.valid := RegEnable(s2_allocatableSlots =/= 0.U, io.s2_fire)
resp_meta.allocate.bits := RegEnable(s2_allocEntry, io.s2_fire)
若使用了altpred,且altpred预测错误,需要更新altpred:
when (usedAltpred && updateMisPred) { // update altpred if used as pred
updateMask(altProvider) := true.B
updateUMask(altProvider) := false.B
updateCorrect(altProvider) := false.B
updateOldCtr(altProvider) := updateMeta.altProviderCtr
updateAlloc(altProvider) := false.B
updateTarget(altProvider) := updateRealTarget
updateOldTarget(altProvider) := updateMeta.altProviderTarget
}
对最长预测的更新中,需要注意的是,若最长预测与备选预测相同,则useful域保持。若最长预测与备选预测不同,则需要根据最长预测是否正确来更新useful域:
updateU(provider) := Mux(!updateMeta.altDiffers, updateMeta.providerU, !updateMisPred)
updateCorrect(provider) := updateMeta.providerTarget === updateRealTarget
updateTarget(provider) := updateRealTarget
updateOldTarget(provider) := updateMeta.providerTarget
updateOldCtr(provider) := updateMeta.providerCtr
updateAlloc(provider) := false.B
若预测失败且并不是最长预测正确但因为信心不足没有采用时,需要判断是否进行allocate:
when (updateValid && updateMisPred && !(providerCorrect && providerUnconf)) {
val allocate = updateMeta.allocate
tickCtr := satUpdate(tickCtr, TickWidth, !allocate.valid)
when (allocate.valid) {
updateMask(allocate.bits) := true.B
updateCorrect(allocate.bits) := true.B // useless for alloc
updateTarget(allocate.bits) := updateRealTarget
updateAlloc(allocate.bits) := true.B
updateUMask(allocate.bits) := true.B
updateU(allocate.bits) := false.B
}
}
这里需要注意的是,每次无法allocate都会递增tickCtr。当tickCtr饱和时,需要对ITTAGE所有表的useful域进行重置:
when (tickCtr === ((1 << TickWidth) - 1).U) {
tickCtr := 0.U
updateResetU := true.B
}
RAS
源代码:/xiangshan/frontend/RAS.scala
RAS专用于预测ret类的jalr指令,其主体就是一个用于记录return地址的栈,其组成比较简洁。
RASEntry
RASEntry中定义了RAS stack中的entry:
class RASEntry()(implicit p: Parameters) extends XSBundle {
val retAddr = UInt(VAddrBits.W)
val ctr = UInt(8.W) // layer of nested call functions
}
retAddr: 函数调用返回的地址ctr: 8位计数器,用于处理递归调用的情景
RASStack
RAS栈深度为32:
val stack = Mem(RasSize, new RASEntry) // RasSize = 32
RAS栈的组成很简单,本身就是一个32个entry的寄存器组,配合一个top以及write_bypass_entry的寄存器组成。top寄存器指向当前RAS栈顶的entry,而write_bypass_entry则保存上一个周期要写入到栈中的entry。也就是说,entry要写进去stack,首先需要先写到write_bypass_entry中,然后再写入到stack中。
val sp = RegInit(0.U(log2Up(rasSize).W))
val top = RegInit(RASEntry(0x80000000L.U, 0.U))
val topPtr = RegInit(0.U(log2Up(rasSize).W))
val wen = WireInit(false.B)
val write_bypass_entry = Reg(new RASEntry())
val write_bypass_ptr = Reg(UInt(log2Up(rasSize).W))
val write_bypass_valid = Reg(Bool())
when (wen) {
write_bypass_valid := true.B
}.elsewhen (write_bypass_valid) {
write_bypass_valid := false.B
}
压栈与弹栈的操作比较简单,与一般数据结构中的并无区别,在这里不再赘述。需要注意的是recovery机制,这个细节将会在RAS top中提到。
RAS Top
Recovery机制
当在s3阶段判定需要push/pop时(SC矫正TAGE预测结果后),s2没有进行push的call指令或者没有进行pop的ret指令需要重新执行一次,或者当后端返回miss predict的call或者ret时,都需要进行recovery:
val s3_recover = io.s3_fire && (s3_pushed_in_s2 =/= s3_push || s3_popped_in_s2 =/= s3_pop)
io.out.resp.s3.rasSp := s3_sp
io.out.resp.s3.rasTop := s3_top
val redirect = RegNext(io.redirect)
val do_recover = redirect.valid || s3_recover
val recover_cfi = redirect.bits.cfiUpdate
val retMissPred = do_recover && redirect.bits.level === 0.U && recover_cfi.pd.isRet
val callMissPred = do_recover && redirect.bits.level === 0.U && recover_cfi.pd.isCall
对于s3的recovery比较简单,只需要把本该push或者pop的操作做了就可以,而后端的recovery则要根据后端返回的recover_cfi信息进行recovery:
spec_ras.recover_valid := do_recover
spec_ras.recover_push := Mux(redirect.valid, callMissPred, s3_push)
spec_ras.recover_pop := Mux(redirect.valid, retMissPred, s3_pop)
spec_ras.recover_sp := Mux(redirect.valid, recover_cfi.rasSp, s3_sp)
spec_ras.recover_top := Mux(redirect.valid, recover_cfi.rasEntry, s3_top)
spec_ras.recover_new_addr := Mux(redirect.valid, recover_cfi.pc + Mux(recover_cfi.pd.isRVC, 2.U, 4.U), s3_spec_new_addr)